Describe a Network Solid and Give Two Examples
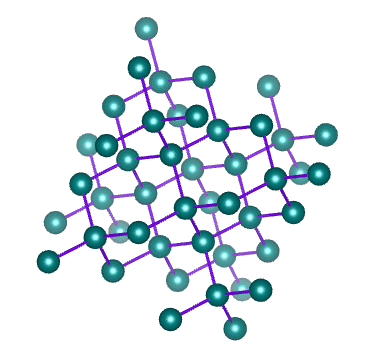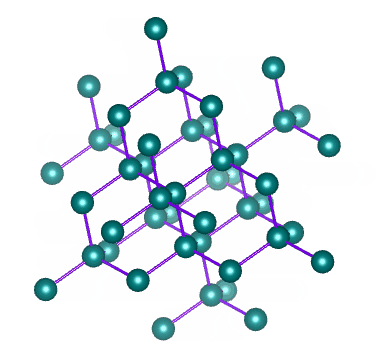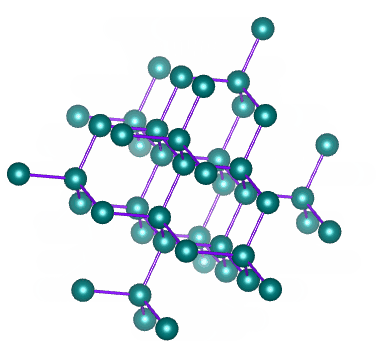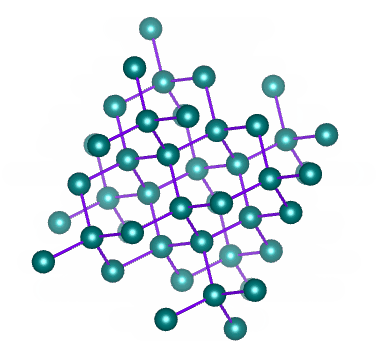
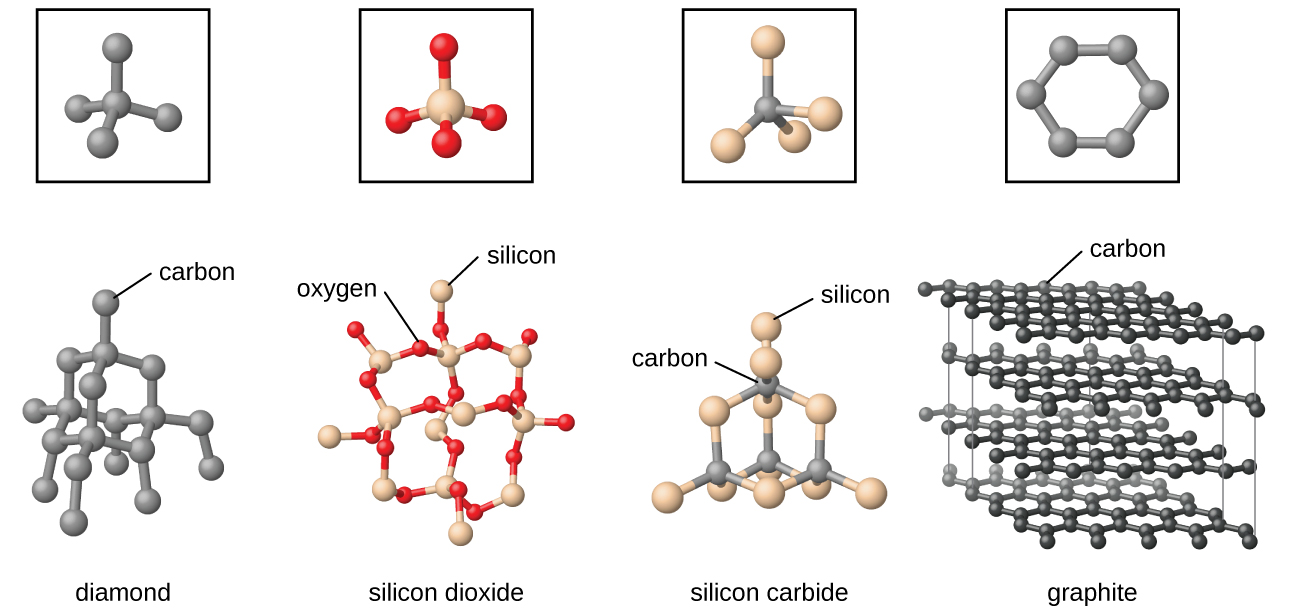
Examples of network solids include diamond with a continuous network of carbon atoms and silicon dioxide or quartz with a continuous three dimensional network of SiO 2 units. Foreign metal ions in quartz produce semiprecious stones such as emerald amethyst and garnet.
![]()
How To Identify Covalent Network Solids Chemistry Study Com
Examples of network solids include diamonds amethysts and rubies.
. Usually covalent network solids have relatively high melting and boiling points. Wide Area Network A network that covers multiple cities such as the network of a regional or national telecom company. Network solids are substances in which all of the atoms are covalently bonded to each other.
They take higher temperatures to melt because melting them requires breaking these covalent bonds. Diamonds are network solids made of carbon atoms. Each silicon is tetrahedrally bonded to four oxygen atoms.
Quartz A large 3-dimensional network with silicon and oxygen. Network Solids of Silicon Silicon makes up 257 of the Earths crust. For example carbon can form two different network solids.
Network solids are hard and brittle with extremely high melting and boiling points. Describe a network solid and give two examples. Covalent compounds exist as molecules made of two or more atoms joined together.
Melting a network solid would require breaking covalent bonds throughout the solid How does a network solid differ from most other covalent compounds. In diamond the bonding occurs in the tetrahedral geometry while in graphite the carbons bond with each other in the trigonal planar arrangement. Two examples are diamond and silicon carbide.
Covalent compounds are the substance that is made generally by bonding between two or more non-metals. Quartz is a network solid made of continuous SiO 2 subunits. Network solids include diamond quartz many metalloids and oxides of transition metals and metalloids.
The drought most commonly known covalent network solids are unique in beauty diamond type and silicon dioxide SiO 2. You meet and carried out a network solid and describe give two examples include polythene. A network that covers a metropolitan area such as a broadband cellular network that provides mobile web and IP telephony for an entire city.
Network Solid Examples. These materials are made up of only carbon atoms that are arranged in two different ways. All atoms are covalently bonded diamond silicon carbide know the difference between sigma and pi bonds and location.
163 Ionic Metallic and Network Condensed Phases CK-12. Furthermore these solids can occur in two ways. Diamond is a three-dimensional crystal that is the hardest known natural material in the world.
O Si O O O Si OSi O O O O O. A silicon crystal is another example consisting of Si atoms. Describe a network solid and give two examples.
A network solid is a solid in which all the atoms are covalently bonded to each other. Solids in which all of the atoms are covalently bonded to each other as a result they are very stable. As crystalline solids or amorphous solids.
Being composed of atoms rather than ions they do not conduct electricity in any state. NCERT Solutions for Class 12th Chemistry Chapter 1 The. In contrast graphite is a two-dimensional network solid.
The carbon atoms essentially form flat sheets. Solids are divided into two main categories crystalline solids and amorphous solids based on how the particles are arranged. Two examples would be diamond and graphite Molecules of carbon dioxide and water have different shapes even though they both have three atoms.
Two Allotropes of CarbonThese two allotropes of carbon are covalent network solids which differ in the bonding geometry of the carbon atoms. Describe a network solid and give two examples. Melting these substances requires breaking covalent bonds throughout the solid.
Graphite a consist of continuous two dimensional layers covalently bonded within the layer with other bond types holding the layers together. A suitable example for a network solid is diamond with covalently bonded carbon atoms which forms a strong 3D structure.

No comments for "Describe a Network Solid and Give Two Examples"
Post a Comment